Eclipse on Vista

New Eclipse WPF port
Eclipse is now available on Windows Presentation
Foundation (WPF), a new window system that comes pre-installed on Microsoft Windows Vista.
This port is in early access form for 3.3. While this port is stable enough for
exploration and development, it has not yet matured to the level of stability
and performance you have come to expect from the Eclipse platform. Stay
tuned for more improvements on this platform in future releases.
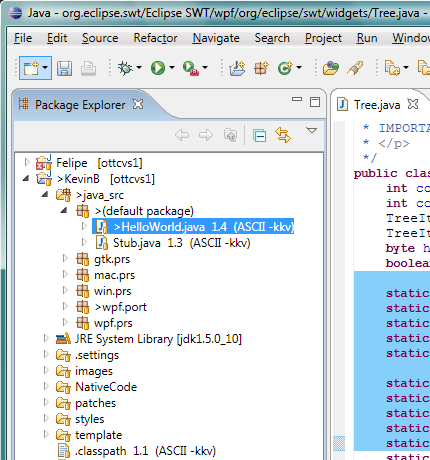
Quick access
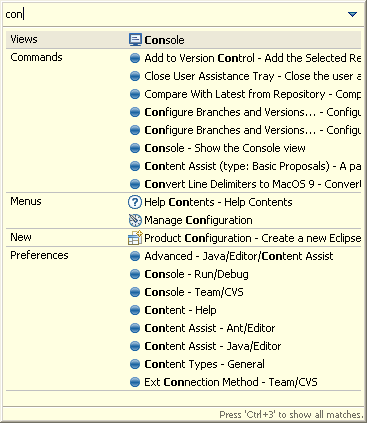
Your previous choices will be remembered and shown the next time the dialog opens. If you enter the same filter string again, the entry you picked last time will be selected automatically.
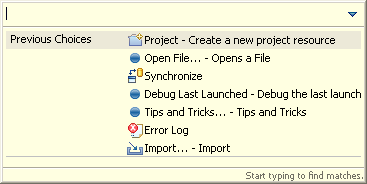
Using the initials of the words you are trying to find, you can narrow down your choices using very few letters.
Undo support for resource operations
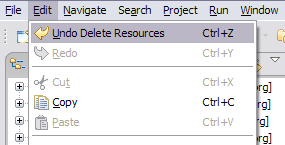
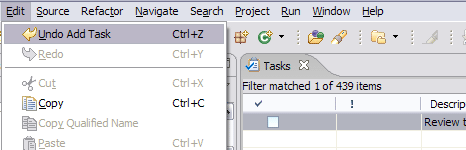
Undo support for task and bookmark operations
A new look
- New Minimize/Maximize behavior. The new 'Minimize' behavior is to move the view stack to the nearest trim area, showing a 'Restore' button along with the icons for the views in the stack. When in the trim, clicking on a view icon will show the view as a fast view. Minimized stacks can be drag and dropped to new locations along the workbench trim. Maximization of any stack triggers minimization of all others. Maximizing an editor now maximizes the entire editor area, allowing you to view multiple editors side-by-side while maximized.
- New workbench tab treatments. Workbench tabs have a new color scheme based on your system title background color, and unselected tabs now also have rounded corners to match the appearance of selected tabs. When tabs become crowded, they now maintain their icon and no longer show an ellipsis in order to maximize the amount of useful information.
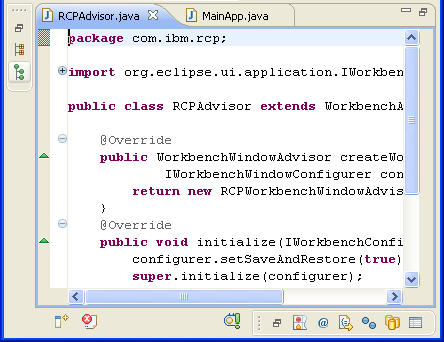
You can reinstate the old presentation via the General > Appearance preference page.
Improved workspace switching
When you switch workspaces you can now transfer some of your current settings with you. The most recently used workspaces now appear on the file menu under the Switch Workspace item for quick access.
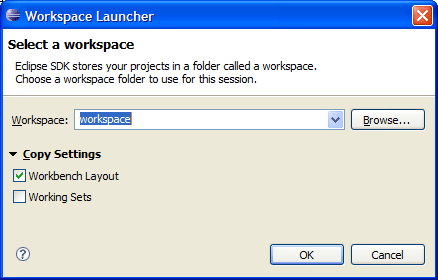
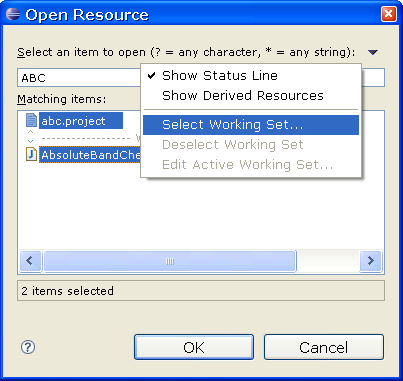
Improved resource selection dialog
The dialog also now shows the history of recently opened items, and allows multi-selection to open several resources at once.
All plug-ins are now signed
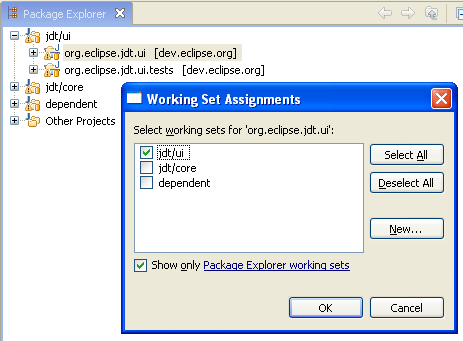
Working set usability improvements
Hiding the window toolbar
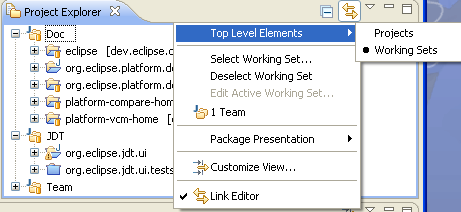
Working sets for the Project Explorer
The Project Explorer can now group and filter elements by working set. You can display working sets as top-level groupings or aggregated into a flat list. The window working sets can also be selected and grouped or aggregated based on a preference.
Patch wizard improvements
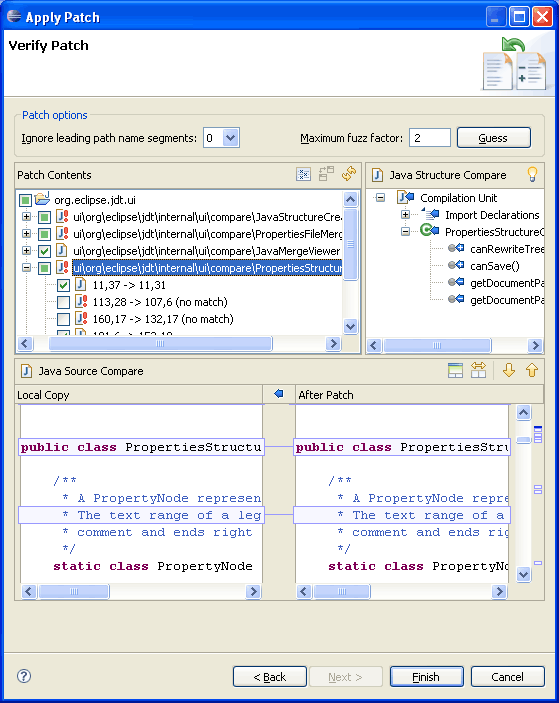
Compare editor improvements
- The contents of compare editors are now kept in sync with other editors currently open on the same file.
- Comparisons that used to take a long time now take a matter of seconds, thanks to a new text differencing algorithm.
- Compare editors are now initialized in the background so that the UI remains responsive while the files are being fetched and compared.
- Many of your favorite editor commands are now available in compare editors, including find/replace, show whitespace characters, show line numbers, and the Show In sub-menu.
- Compare editors now highlight individual changes within a block of changes.
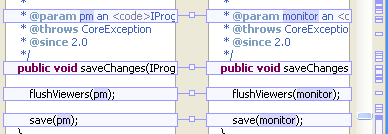
Compare Structure in Outline view
Long resource paths on Windows
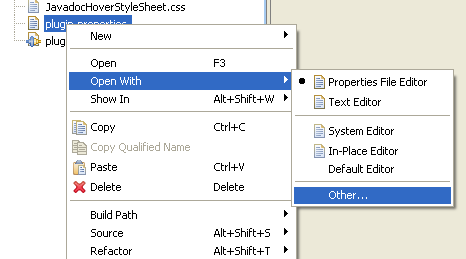
Open files with other editors
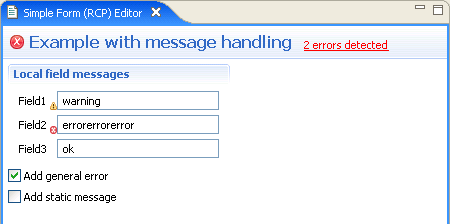
Forms enhancements
Platform level proxy and SSH2 settings
In addition, the JSch SSH2 client used by the Eclipse CVS client has been pushed down to the Eclipse Platform so that it can be used by other clients as well. Use the new General > Network Connections > SSH2 preference page to configure it.

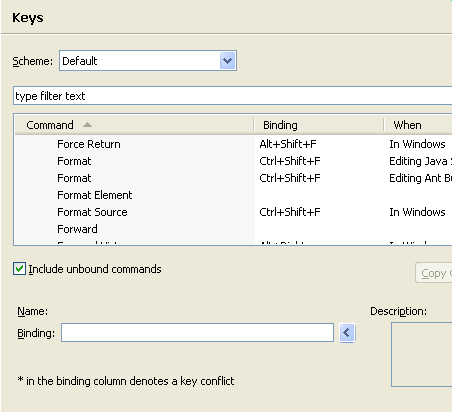
Keys preference page improvements
You can now:
- Update a selected binding immediately by modifying the Binding or When fields
- Create a binding from a command by modifying the Binding field
- Create a command from a binding using the Copy Command button
- Remove all changes from the system with Restore Defaults
Editor area drag and drop
Dragging external files (i.e., from the Windows file explorer) on to the editor area of a workbench window has the same effect as Open File. Also, you can now drag an editor between workbench windows associated with the same workspace.
Properties view make over
The Properties view has adapted to the new look and feel of UI forms. Visual enhancements include new title bar layout, colors and gradient, and new tab design and colors.
Console launcher for Windows
Improved detection of Mozilla plug-ins
MOZ_PLUGIN_PATH. For example:
export MOZ_PLUGIN_PATH=/usr/lib/browser-plugins
Easier help navigation

Help search term highlighting
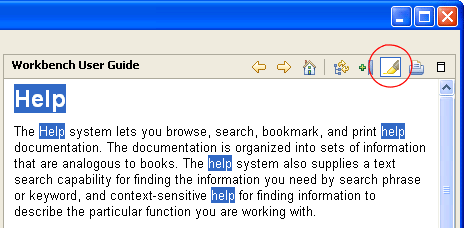
Categorized help search
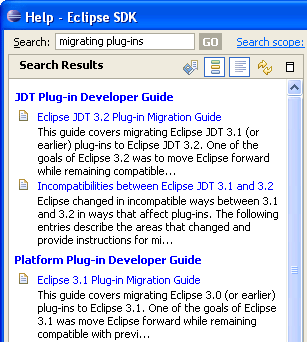
Print multiple help topics
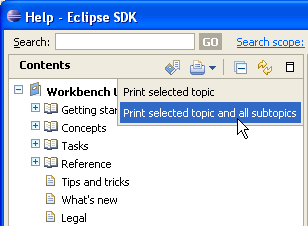
Cheat sheet improvements
Sub steps in a cheat sheet are now clearly separated using horizontal lines. Sub steps can now be previewed. The background colors in the cheat sheet view have been adjusted to make the active step stand out more.
Spell checking in text editors
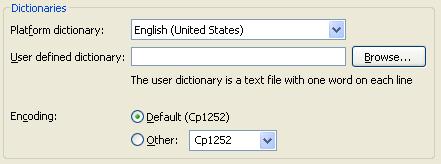
Spell checking is now enabled per default. If you're already a spelling whiz, you can disable this feature with the new Disable Spell Checking quick assist.
Show invisible whitespace characters
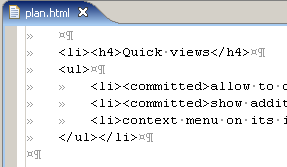
This feature can either be controlled via General > Editors > Text
Editors >
Show whitespace characters preference, or via the [ ] tool bar button when the Editor Presentation action set
is enabled.
] tool bar button when the Editor Presentation action set
is enabled.
Text drag and drop in text editors

You can control this via General > Editors > Text Editors > Enable drag and drop of text preference.
Scroll by pages using Ctrl + mouse wheel
Select by word or line using the mouse
Smart Home/End
This feature can be controlled via General > Editors > Text Editors > Smart caret positioning at line start and end preference.
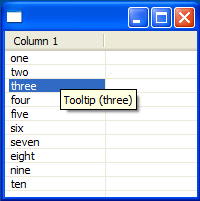
More team annotation options
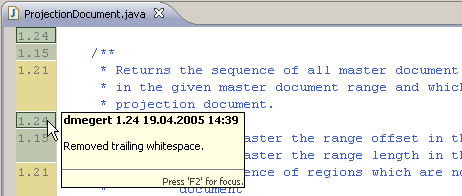
Below we see the author names, with background colored by date. These options are configurable via the ruler context menu (Ctrl+F10):
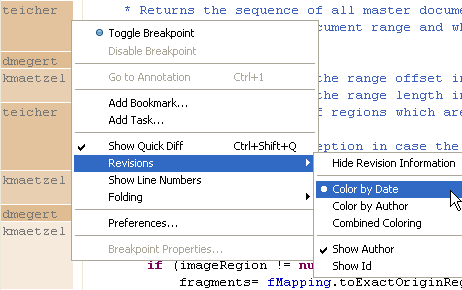
Recenter command
Joining lines in text editors
Convert tabs to spaces
This feature can be enabled via General > Editors > Text Editors > Insert spaces for tabs preference.
More flexible templates
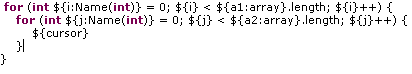
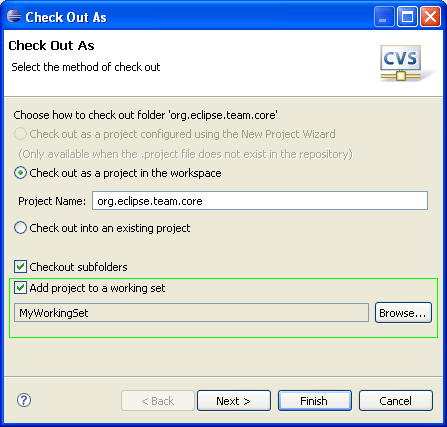
Import CVS projects directly into working sets
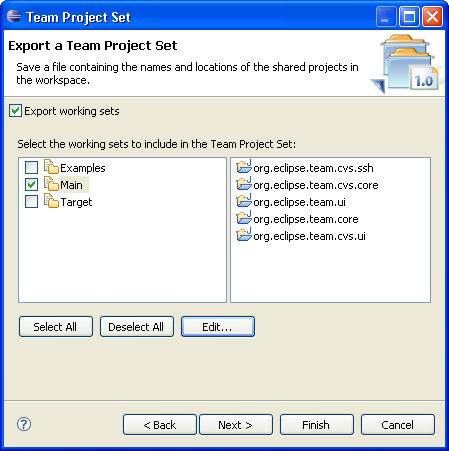
Export working sets as part of team project set
History view search
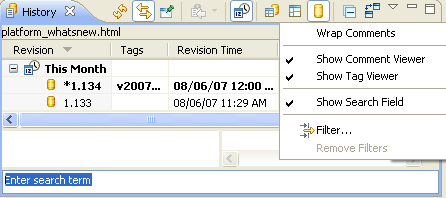
History view now has view history
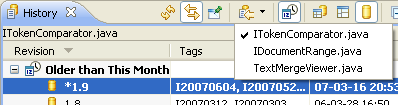
Spell check in Commit dialog
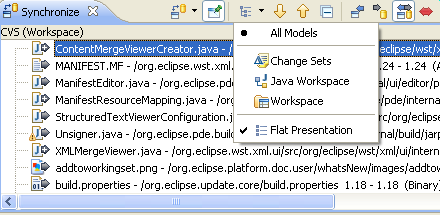
Flat presentation in model-based synchronizations
Launch selection vs. launch last
Running and debugging applications has been simplified to run or debug the selected file or active editor. Use the Launch the selected resource or active editor preference to enable this behavior on the Run/Debug > Launching preference page. When the selected resource (or active editor) is not executable, you can opt to launch the associated project or launch the previously launched application.

Pressing the Run or Debug toolbar button will launch the selected resource (as will the Run or Debug action in the top level Run menu). When a launch configuration does not exist for a file and there is only one way to launch it, the file will simply be launched in the mode you selected. When there is more than one way to launch a file you will be prompted to select how to run or debug the application. For example, when running a JUnit test you can run as a Java application or JUnit test. A launch configuration will be created and an entry will be added to the launch history for the application.
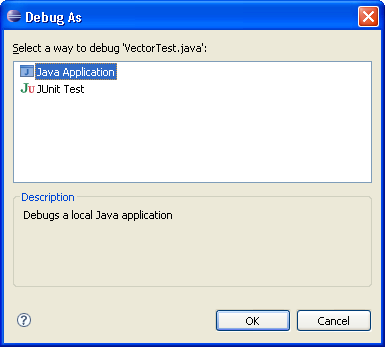
When the same file is launched again, the most recent configuration
in the launch history associated with that file is re-launched.
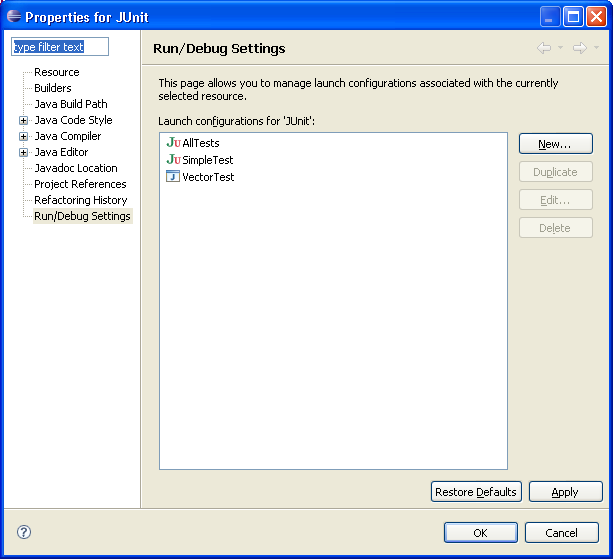
Run/Debug settings
A new properties page has been added to manage launch configurations associated with a resource. For example, selecting the Run/Debug Settings property page for a project will display all launch configurations associated with that project. Configurations can be created, deleted, and edited from this page.
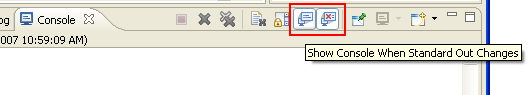
Automatically showing console
Toggle buttons have been added to the console toolbar controlling when the console is automatically displayed. The buttons provide quick access to the workspace preferences to show the console when output is written to standard out or standard error (also available from the Run/Debug > Console preference page).
Refactoring without save
Refactorings don't require all editors to be saved any more. They can now operate even if Java or text editors still have unsaved changes. If you don't like unsaved editors after refactorings, you can still choose to always save modified resources on the Javapreference page.
Rename refactoring in editor
The Java Rename refactoring can now be performed directly in the editor, without showing a dialog.
When using Refactor > Rename (Alt+Shift+R) in the Java editor, the editor enters linked mode instead of opening a modal dialog. Changes stay local until Enter is pressed, which will perform the change in the whole workspace.
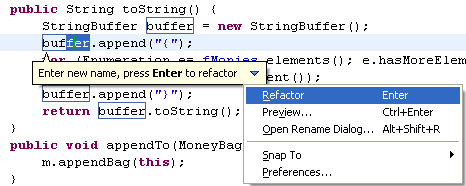
To see and configure refactoring options, press Alt+Shift+R again, or click the menu button and choose Open Rename Dialog....
If you prefer the old modal dialog, you can disable Rename in editor without dialog on the Java preference page.
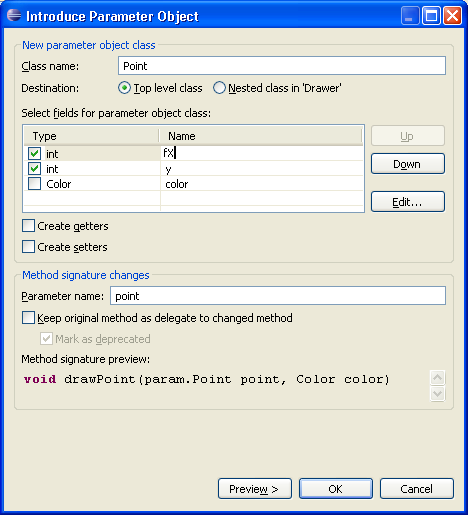
Introduce Parameter Object refactoring
Introduce Parameter Object is a new refactoring that replaces a set of method parameters with a new container object. All calls to the method are updated to pass the new parameter object class.
Use cases:
- group parameters which logically belong together; e.g., Date start, Date end, String newValue, String oldValue
- reduce number of parameters
- provide useful defaults in the parameter object
- pass the parameter down the call chain
To execute the Introduce Parameter Object refactoring, select a method, invoke Refactor > Introduce Parameter Object, select the parameters that should be used as fields, and give meaningful names.
The following code snippet

will be modified to

Sort Members on multiple elements
The Sort Members action can now sort multiple elements at once. Select a package, a project, or a set of Java elements in the Package Explorer and invoke Source > Sort Members.

Clean Up profiles
A preference page has replaced the Source > Clean Up wizard. Clean Up profiles can be defined on this preference page. A profile can be attached to the workspace or to individual projects. Project settings can be shared in a team through a version control system. It is also possible to export and import each profile.
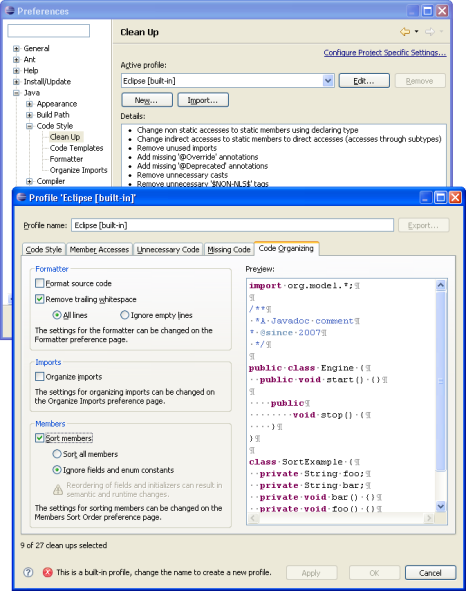
New clean ups
The following Clean Ups have been implemented:
- Format source code: The formatting settings can be configured on the Formatter preference page.
- Remove trailing whitespace: You can choose to remove trailing whitespace on all lines or to ignore empty lines.
- Organize imports: Imports are organized according to the settings for the project or workspace.
- Sort members: You can sort either all members of a compilation unit, or ignore fields, enum constants, and initializers (because sorting such members may result in semantic changes).
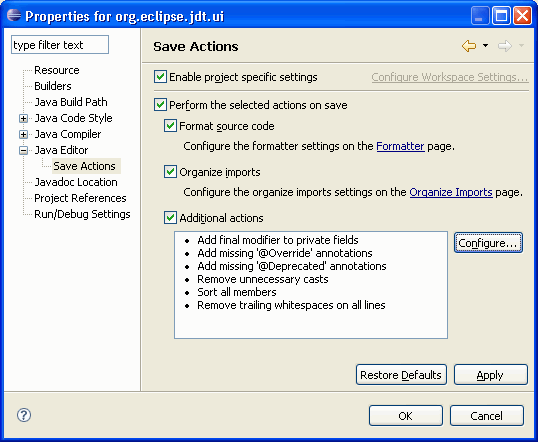
Code clean up on save
It is now possible to automatically invoke code clean up whenever the Java editor is saved. This feature can be enabled globally on the Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page. The save actions can also be configured per project, which makes it easy to enforce a project-wide standard by sharing the settings across a team:
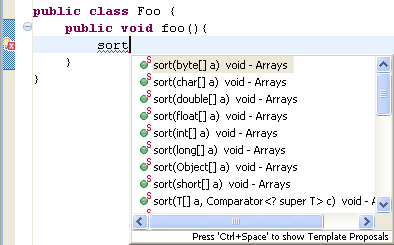
Content assist for favorite static imports
The Content Assistant (Ctrl+Space) can now propose completions for static members from a list of favorite imports that can be configured on the Java > Editor > Content Assist > Favorites preference page.
For example, if you have added java.util.Arrays.* to
this list, then all static methods of this type matching the completion
prefix will be added to the proposals list:
The import preferences from the Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page are honored when inserting such a proposal.
Content assist for variable with unresolved type
The Java editor now supports the new member proposals with unresolved types: depending on the Java > Editor > Content Assist > Add import instead of qualified name preference the editor will either automatically add imports or fully qualify the types for such proposals.
Pressing ; in the following scenario:
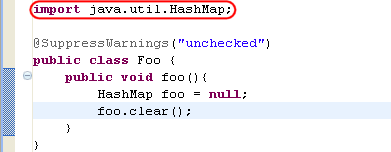
results in:
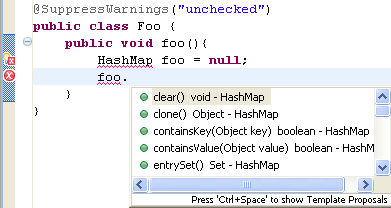
Content assist provides declaration proposals for undefined local variables
Code assist can now infer the name of a declared local variable by detecting the presence of unresolved names in subsequent code, as shown in the example below:
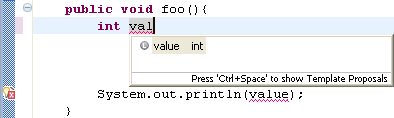
Content assist improvements continued
- Content Assist (Ctrl+Space) inside a try-catch clause can now infer exception type names based on exceptions detected to be thrown in the corresponding try block. These exceptions are now listed before other possible exceptions.
- When completing a name reference, Content Assist now proposes unresolved names found in other parts of the code.
- Code completions in the empty statement now include the local types of the current compilation unit in the list of proposals.
- Code completion after an at sign "
@"proposes all visible annotation types. - Completing in an annotation member proposes all possible attributes which are not already specified.
Quick assists
Functionality that was previously only available in the Refactoring menu is now also offered as quick assists (Ctrl+1). As always, quick assists don't show a dialog, but enter the linked mode where you can change names or types that have been introduced.
- Extract to local variable and Extract to constant: select an expression in the code
- Inline local variable: available on a variable name
- Convert local variable to field: available on a variable name

- Convert anonymous to local type: available on the type name of an
anonymous class
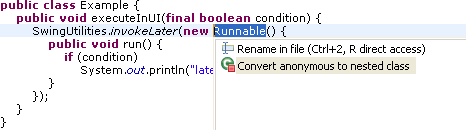
When applied, use the Tab key to navigate through the generated code and to modify the new type name and choose from the offered field and parameter names.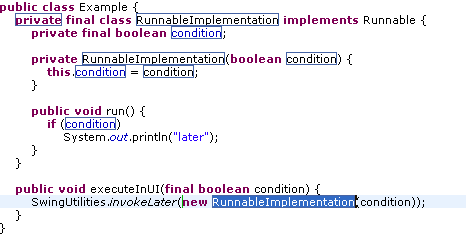
Quick fix to create method from @Override
When you add an @Override annotation to a method that does not override yet, quick fix (Ctrl+1) will offer you to create the method in one of the super types.
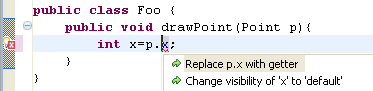
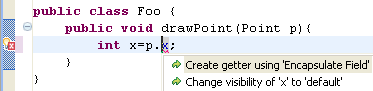
Quick fix to create and use getter and setter
A new quick fix is available for a field not accessible due to visibility restrictions. In the following scenario, use Ctrl+1 to invoke quick fix:
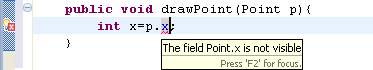
If a getter exists for this field, you can choose to use it.
And if there is no getter for this field, you can choose to create one.
Template for adding JUnit 4 test methods
A new Test template has been added to speed up adding JUnit 4 test methods.
Syntax coloring for brackets
Brackets may now be colored separately from operators in the Java editor via the Java > Editor > Syntax Coloring preference page:

No more "I don't see the full source" questions on the newsgroup
The command group that contains the Show Source
of Selected Element Only tool bar button  is now hidden by default. The setting can be toggled using the Java > Editor
> Only show the selected Java element preference.
is now hidden by default. The setting can be toggled using the Java > Editor
> Only show the selected Java element preference.
Configurable Javadoc font
The font for displaying Javadoc is now configurable on the General > Appearance > Colors and Fonts preference page. The Javadoc display font is used by the Javadoc view and hover, and for the additional information shown during content assist.

Background color for source hovers
The background color for all hovers that show source in the Java editor can now be configured on the Java > Editor preference page.
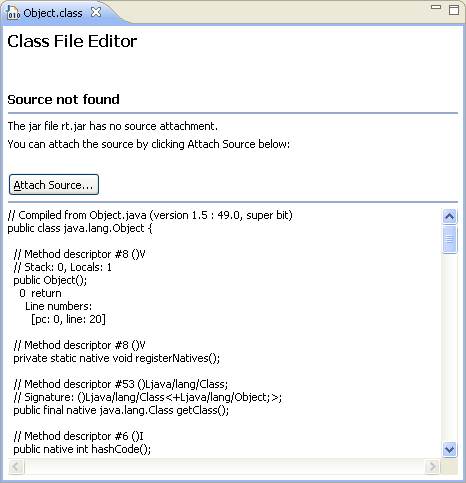
Class file editor shows disassembled code
The Java class file editor now shows the disassembled bytecodes when source code is not available.
Improved handling of duplicate local variables and types
JDT now does a better job of handling invalid code with duplicate local variables and types; in particular it will minimize secondary errors. This allows the Java tools to perform in offending code, so as to offer quick fixes.
- Local rename (Ctrl+2,R) can now operate even in faulty nested loops,
allowing you to quickly fix the name of the duplicate variable in all
the places it appears.

- Method invocation or field access through a duplicate variable now
refers to nearest definition of the local variable, thus reducing the
number of secondary errors reported.

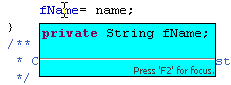
Improved null check detection
The existing Null reference option on the Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings preference page has been split into three options:
- Null reference (in 'Potential programming problems')
When this option is enabled, the compiler will issue an error or warning whenever a variable that is statically known to hold a null value is used to access a field or method, as shown in the example below: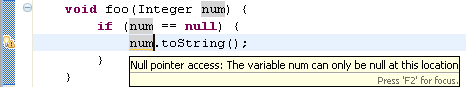
- Potential null reference (in 'Potential programming problems')
When this option is enabled, the compiler will issue an error or a warning whenever a variable is statically known to potentially hold a null value, as shown in the example below: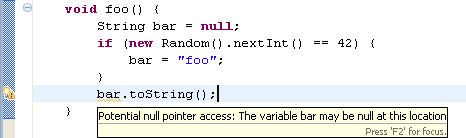
- Redundant null check (in 'Unnecessary code')
When enabled, the compiler will issue an error or a warning whenever a variable that is statically known to hold a null or a non-null value is tested against null, as shown in the examples below: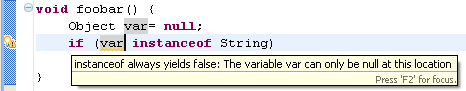
Warning for raw types activated by default
The optional compiler diagnostic for detecting any usage of a raw type is now activated by default.
This diagnosis can be configured on the Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings preference page, using the Generic types > Usage of a raw type preference.

Unused parameter warning enhancement
The Unused Parameter warning was improved with a new option that helps avoiding false positives. You can give the compiler a hint that a parameter is not really unused by commenting it with a @param tag.
The option is located on the Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings preference page in the Unnecessary code section.

Colored labels in Java views
To enable colored labels in Java views, open the Java > Appearance preference page and select Use colors in labels.
Decorations for transient and volatile fields
Transient and volatile fields now have corresponding icon decorations:

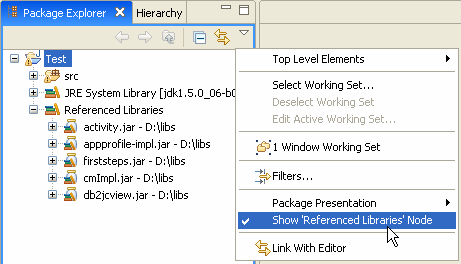
Grouping of JARs and class folders in Package Explorer
The Package Explorer now groups referenced libraries in a new container node.
More Java search options
The Java search dialog has been extended to offer finer control to limit the scope to search in sources, required projects, JRE libraries, and application libraries.
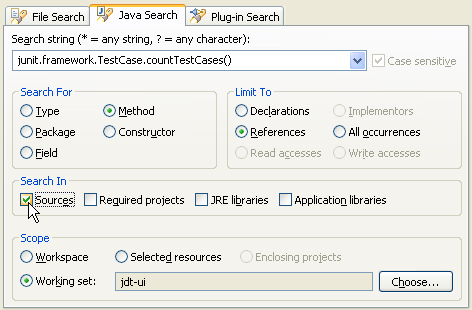
Search filter for references to overridden method
The Java search engine has introduced a new criterion for categorizing method reference matches. It can now distinguish an invocation via a type or one of its subtypes from an invocation via a supertype, which is usually a weaker match. The Search view now includes a filter for further narrowing references to the searched method.
In the following example, the user searched for references to the A.toString() method
and got 3 matches. Since o.toString() denotes an invocation
of a method that is overridden by the search target A.toString(),
it can be filtered out from the Search
view by activating the "References to Overridden" filter as shown below:
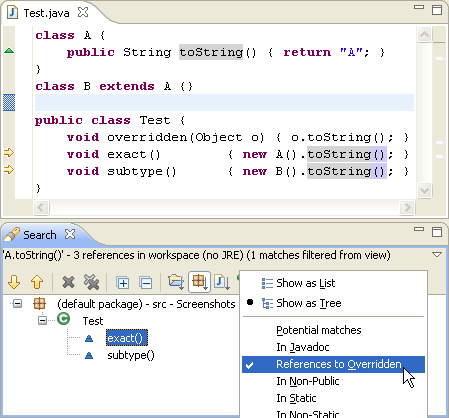
Select execution environment when creating Java project
When you create a Java project that you want to share with a team, it is a good idea to use an execution environment instead of a specific JRE.
Execution environments are symbolic representations of JREs with standardized entries like 'J2SE-1.4', 'J2SE-1.5'. That means no file system path will go into the shared build path.
JREs can be assigned to the environments on the Java > Installed JREs > Execution Environments preference page.
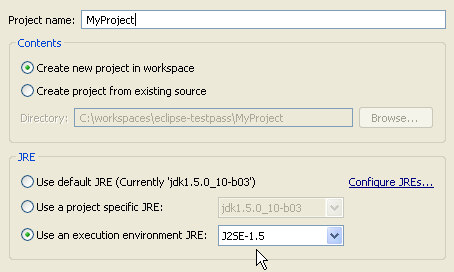
Add new Java project to a working set
The New Java Project wizard got additional input fields to specify the working sets to which the new project gets added. The fields are initialized from the current selection or the active working set filter in the Package Explorer.
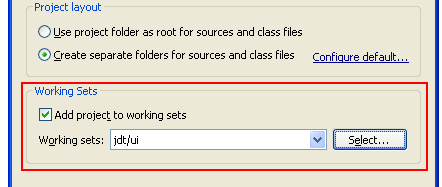
Assign working sets
It's easier now to reorganize Java elements or resources in working sets. To assign an element to a different working set, select the element in the Package Explorer and choose Assign Working Sets... from the context menu.
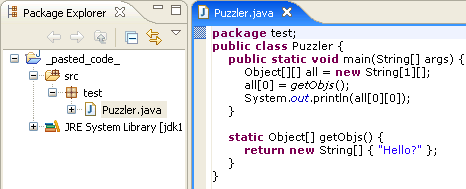
Paste type declaration creates new project
Ever wanted to quickly try out a code snippet somebody sent to you? Copy the snippet to the clipboard, go to the Package Explorer, make sure nothing is selected, and choose Edit > Paste (Ctrl+V).
Eclipse will try to parse the text in the clipboard, and if it looks like contents for a *.java file, it will create a new Java project and create the *.java file.
Like in 3.2, you can, of course, still select an existing project or package as target for the new file.
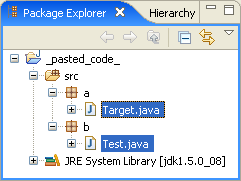
Enhanced paste in Package Explorer
Pasting Java source text with multiple package declarations to the Package Explorer now automatically creates all the necessary packages and compilation units. The structure on the right is created when you paste the snippet on the left into the Package Explorer while nothing is selected:
package a;
public class Target {
}
//--
package b;
import a.Target;
public class Test {
void reference() {
new Target();
}
}
|
 |
Undo deletions in Java Views
Edit > Undo is now also available for deletions of Java elements in Java views. Accidentally deleted packages, compilation units, etc. can easily be restored by pressing Ctrl+Z.
Java drag-and-drop for Project Explorer
Java elements dragged and dropped in the Project Explorer now trigger Java refactoring events (like in the Package Explorer).
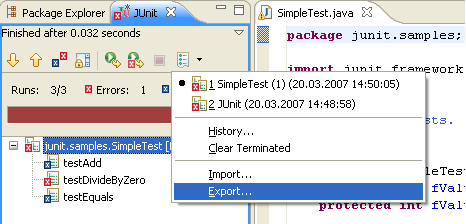
Export and import JUnit test runs
JUnit test runs can now be exported and imported.
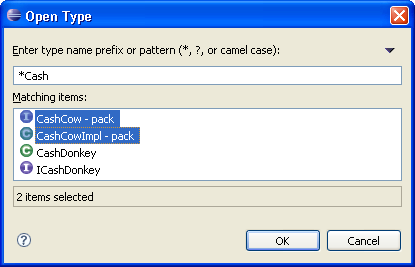
Open Type opens multiple types
The Open Type dialog (Ctrl+Shift+T) now supports opening multiple editors at once.
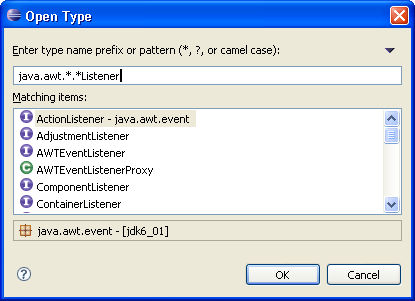
Package and enclosing type pattern search
Patterns with '*' or '?' characters may be specified for packages and enclosing types in the Open Type dialog.
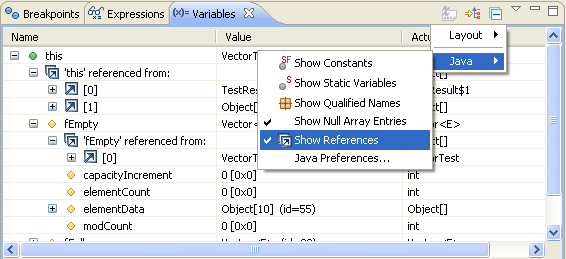
Follow references (Java SE 6 only)
You can display all references to an object (only available when debugging on a Java SE 6 virtual machine). Object references can be displayed in the variables view by toggling the Show References setting in the view menu. References to each object are grouped in a collection.
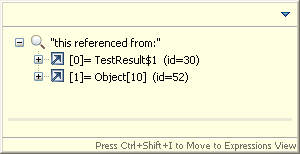
References can also be displayed in a popup dialog by selecting an object in the variables view and choosing All References from the context menu.
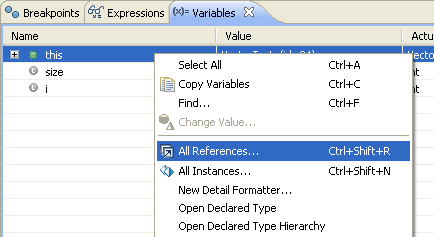
References are displayed in a popup dialog.
Display instances (Java SE 6 only)
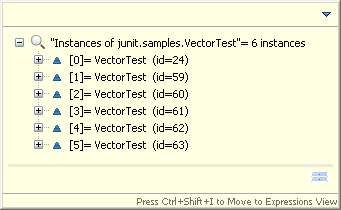
You can display all instances of a Java type (only available when debugging on a Java SE 6 virtual machine). Instances are displayed in a popup dialog by selecting a type in the editor outline, a type name in the Java editor, or a variable in the Variables view and choosing All Instances from the context menu.
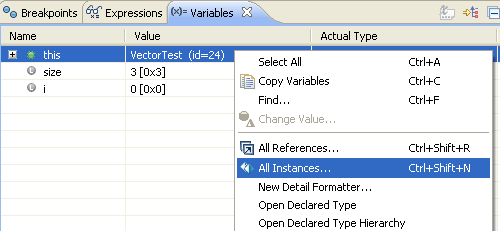
Instances are then displayed in a popup dialog.
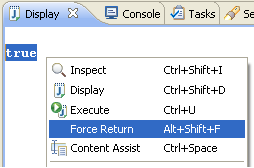
Force return (Java SE 6 only)
You can force an early return from a method (only available when debugging on a Java SE 6 virtual machine). This returns a value from the current stack frame without executing any more instructions in the method and releases any locks obtained by synchronized blocks. A return value is created by selecting an expression and Force Return (Alt+Shift+F). This action is available from the Java editor's context menu, top level Run menu, in the Display view, and in the detail pane of the Variables view.
Forcing an early return from a non-void method requires an expression
to be evaluated. For example, if a method was going to return false
you could return a value of true by selecting an expression in the Display
view and invoking Force Return. In the following example,
elementCount is not equal to zero, and would return false
(see debug hover showing the value of elementCount).
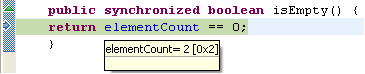
Use the Force Return action from the Display view to return true instead.
Hyperlink stepping
When debugging you can use hyperlinks to step into a method. Use Ctrl+Alt+Click to step into a method (rather than Ctrl+Click which will navigate to the source code).
Double-click and Ctrl+Shift+B for all kinds of breakpoints
Double-clicking in the vertical ruler, or invoking Toggle Breakpoint (Ctrl+Shift+B), now creates an appropriate kind of breakpoint based on the cursor location - line breakpoint, watchpoint, method breakpoint, or class load breakpoint. To create a class load breakpoint, double click on the class declaration line.

Step through filters vs. step return
You can configure step filters to always return from
a filtered location or step through to a non-filtered location. For
example, if java.util is a filtered location, stepping
into code in HashMap could result in a call-back to your
application code to check the equality of an object. If you choose to
Step through filters a step into would end up in your
application code. However, when the Step through filters
option is disabled, a step into HashMap would behave like
a step over.
Use the Step though filters preferences setting on the Java > Debug > Step Filtering preference page to toggle the feature.
Auto format stack traces
Stack traces can be formatted automatically as you paste them into the Java stack trace console. An Auto Format toggle is available on the console tool bar.
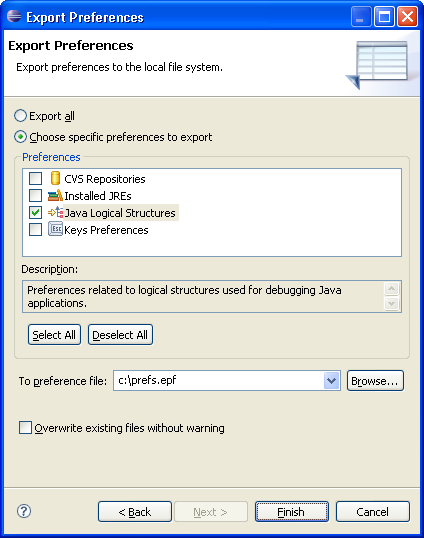
Export logical structures
You can now export and import Java logical structure
preferences separate from other workspace preferences. Java logical
structures are defined on the Java > Debug > Logical Structures
preference page. Logical structures are used to define alternate presentations
for complex data structures and are displayed when examining objects
in the Variables view. For example, displaying a java.util.Collection
as an array rather than revealing the internal data structure that implements
the collection.
New code formatter options
New options have been added to the Java > Code Style > Formatter preference page:
- Comment formatting can now be enabled and disabled
for each comment type individually (Javadoc, block, single line, and header comments).
Block and line comments on the first column can be excluded from indentation.

- The number of blank lines that Organize Imports (Ctrl+Shift+O)
inserts between import groups can be configured on the Blank Lines
tab. When formatting, this setting will take precedence over the number
of blank lines to preserve.
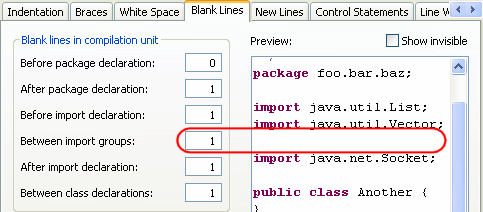
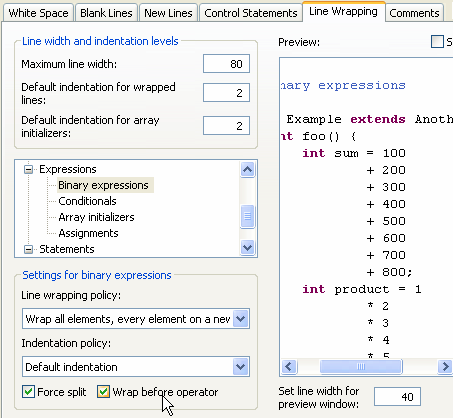
- Binary expressions can now be wrapped before or after the operator.
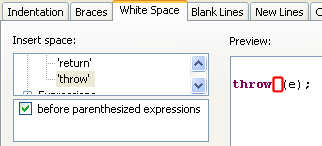
- For return statements, you can now add or remove whitespace before
the parenthesized expression of the throw statement. This option is
available on White Space tab.
Access rules for execution environments
Access rules are now assigned to each execution environment
based on its profile. For example, rules prevent access to com.sun.*
packages that are not guaranteed to be present at runtime. The rules
are only applied to projects that are bound to execution environments.
Projects bound to a specific JRE still have access to all of their libraries.
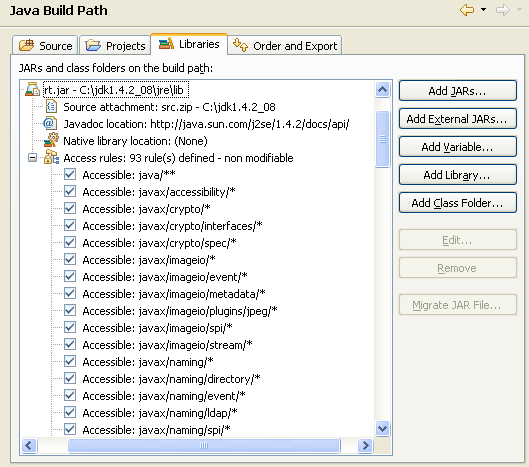
Deprecated and non-modifiable classpath variables
System-defined classpath variables can now
be deprecated and/or declared read-only via the org.eclipse.jdt.core.classpathVariableInitializer extension
point.
Users should replace deprecated classpath variables by better mechanisms such as Libraries.
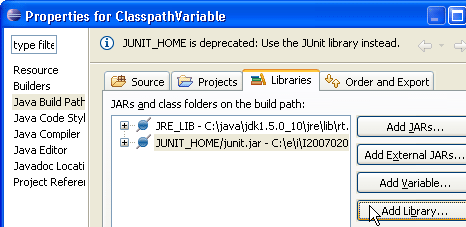
For some variables (e.g. JUNIT_HOME), the Problems view even offers quick fixes to migrate existing projects.
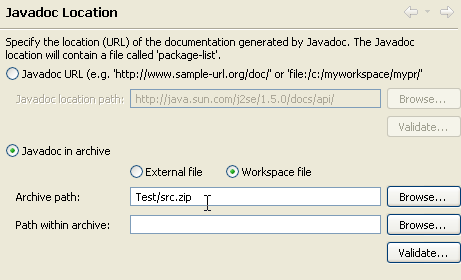
Workspace relative paths for Javadoc location
Workspace relative paths are now accepted as Javadoc locations for archives and class folders:
Runtime type generation
Java 5 annotation processing (APT) was introduced
in Eclipse 3.2, but until now, new types could only be generated by doing
a build. Java 5 Annotation processors can now generate new types on the fly, as
you edit the annotations. This feature is disabled by default, for performance
reasons; to enable it, a processor should include "enableTypeGenerationInEditor"
in the set of strings returned from
AnnotationProcessorFactory.supportedOptions().
Java 6 annotation processing
Eclipse 3.3 fully supports Java 6 annotation processing in the Eclipse Java batch compiler. Java 6 annotation processing is also minimally supported in the IDE, with more support to come in the future.
Custom splash screens

IDE application moved to new plug-in
Advanced tooltips
JFace now supports tooltips that supply a
Composite for more complex tooltips. See org.eclipse.jface.window.Tooltip.
Widget-independent tree and table viewers
A new abstract class AbstractTableViewer has been introduced,
making it possible to create subclasses that work on table widgets other than SWT's
Table. More methods on AbstractTreeViewer have been made
accessible to subclasses for the same reason.
Per-column label providers, improved editing support
AbstractTableViewer and AbstractTreeViewer now inherit
from a new base class ColumnViewer. A new abstraction for columns in viewers
has been introduced, making it possible to use a separate label provider for each column.
After creating a viewer, create appropriate viewer column objects (TableViewerColumn
or TreeViewerColumn) and call setLabelProvider on the column
object rather than the viewer itself. The new column abstraction also makes it easier to
set up an editable table or tree - see ViewerColumn.setEditingSupport(),
and to add keyboard navigation to editable tables or trees - see
TableViewerEditor.create() and TreeViewerEditor.create().
Code examples can be found on the JFace snippets page.
Custom tooltips for tree and table cells
TreeViewer and TableViewer now support custom
tooltips on a per cell basis. See org.eclipse.jface.viewers.CellLabelProvider.
Data binding
Data binding supports automatic synchronization between UI state and model state and drastically reduces the amount of listener code required to implement common UIs. The data binding API was made public in 3.3, and the existing single plug-in was split into three to separate the core framework (org.eclipse.core.databinding) from code that implements binding to SWT and JFace (org.eclipse.jface.databinding) and code that binds to JavaBeans-style models (org.eclipse.core.databinding.beans). See the data binding wiki page for more information.
Status handling
OSGi R4.1
New Application Model
Eclipse applications can now implement org.eclipse.equinox.app.IApplication to take full advantage of the new application model. See the org.eclipse.core.runtime.applications extension point for more details on the options that can be specified for application extensions.
Equinox launcher
Among other advantages, this change allows for SWT widgets to be used in the splash screen. As well, the splash screen can appear much earlier if the product is set up properly.
Equinox HTTP service
Support for Launching Equinox in Application Servers
Orbit project created
Platform proxy settings
JSch SSH2 Client Support
Contribute columns to vertical ruler
Extensible hyperlink detection
Clients can use the org.eclipse.ui.workbench.texteditor.hyperlinkDetectors extension
point to add their own hyperlink detectors and can enable their viewers using the
corresponding methods in the source viewer configuration along with the
org.eclipse.ui.workbench.texteditor.hyperlinkDetectorTargets
extension point.

Mixed mode launch APIs and more
launchDelegates and launchConfgurationTypes extension
points.
ISVs can also contribute one or more tabs to existing tab groups in
the launch dialog to extend existing launch types with new function.
For example, a profiling tool could provide a tab to configure profile
options for Java applications. See the new extension point launchConfigurationTabs.
The platform also allows more than one toolset to exist for launching the same kind of application. For example, two profilers could exist for Java applications and the user would be prompted to choose which profiler to use.
Debug context API
org.eclipse.debug.ui.contexts allowing clients
to listen to and drive the active debug context.Debug command API
org.eclipse.debug.ui.commands.Pluggable detail panes
API has been added to the debug platform
allowing custom detail panes to be contributed to the Variables view.
Clients may use any SWT control to render custom details for their variables.
A context menu allows users to choose between available detail panes
for each variable. See the new extension point org.eclipse.debug.ui.detailPaneFactories.
Remote help content
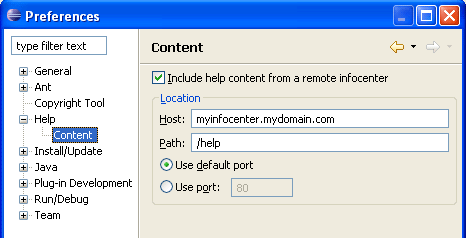
Plug in help in any format
Improved dynamic user assistance content
- Welcome pages (XML or XHTML) and contributions
- Help XHTML topics, table of contents, keyword index, and context-sensitive help
- Cheat sheets, both simple and composite
You can also define your own filter criteria and use boolean operators to achieve greater flexibility with filtering by using XML expressions in any of the documents listed above.
Added control of help/welcome content ordering
Link to anything from context-sensitive help
Compare supports File Buffers
Apply Patch API
Menu Contribution API
Printing support added on GTK+
New DateTime control

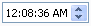
Option to print line numbers added to StyledText
StyledTextPrintOptions.printLineNumbers
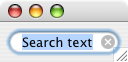
field to true.Text SEARCH style
Text controls
can now have the look and feel of a search field with the SWT.SEARCH style.
Adding the SWT.CANCEL style gives the user a way to cancel
the search. This example
snippet created the Text control shown in the snapshot
below.
System tray support added on Mac OS X
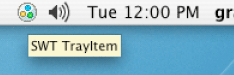
Writing PNGs now supported
Browser profiles on GTK+ and linux-motif
Browser support added on PowerPC
Native GTK Combo box

Faster JPEG/PNG image loading
Color cursors on Mac OS X and GTK

This example snippet created the cursor pictured above.
New graphics line drawing capabilities
LineAttributes class
and the new GC methods get/setLineAttributes.
(This example snippet created the above snapshot.)
SWT libraries automatically found
Mozilla everywhere
SWT.MOZILLA style.
This example
snippet created the snapshot below.

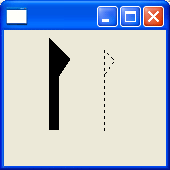
DragDetect API
Control.setDragDetect() to
disable the default drag detection and Control.dragDetect() to
implement their own. For example, a custom list control could start dragging
only when an item is selected. Typed events for drag detection are now
available (see DragDetectListener and DragDetectEvent).
This example
snippet created the snapshot shown below.
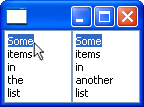
Drag over and drag under effects
DragSourceEffect and DropTargetEffect.
The default effects for the Table, Tree and StyledText controls
have been changed to use these classes (see TreeDragSourceEffect, TreeDropTargetEffect and
the corresponding classes for these controls). This StyledText example
snippet created the snapshot shown below.
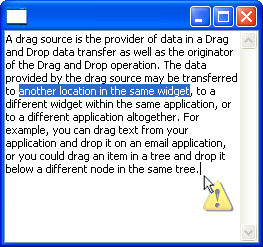
JavaXPCOM support
SWT.MOZILLA-style Browsers can
now be programmed to via JavaXPCOM. This requires that XULRunner 1.8.1.2
or newer be installed.
This example
snippet created the snapshot below.
OLEExample and OLE improvements
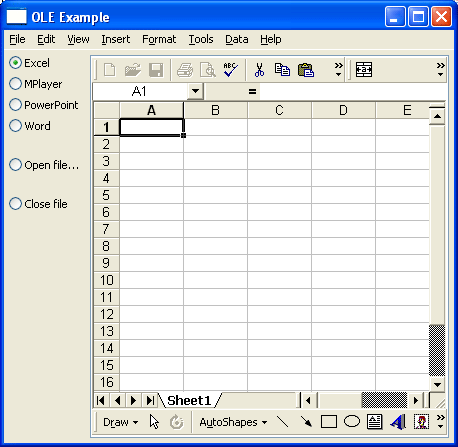
Reparenting support on Mac OSX
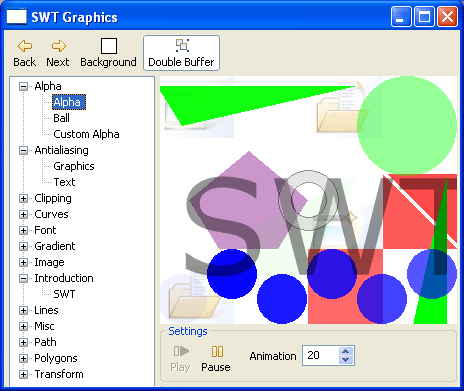
Advanced graphics supports mirroring

SWT graphics showcase
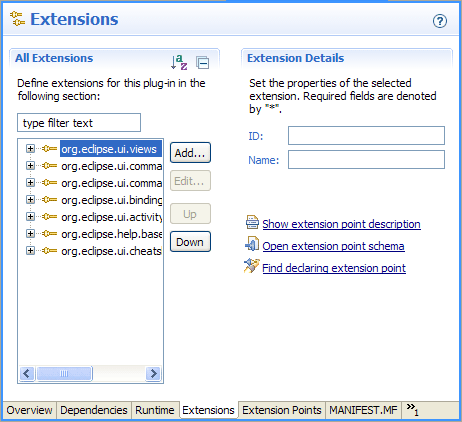
Self-hosting with multiple versions of the same plug-in
Development scenarios where this new support is particularly useful include:
- Workflows that require different plug-ins to compile against different versions of the same plug-in
- Building an update site where you are constantly managing multiple versions of the same plug-in in the workspace
PDE editors facelift
- Gradient form headers
- Form title icons
- New section title bar design and colors
- Section header tool items using standard size icons
- Form header help icons
In addition, all PDE form editor pages comply with the latest UI recommendations for margins and spacing.
Field assist in Forms
This feature works in a similar way to the content assist in the Java editor, and supports package names and CamelCase.
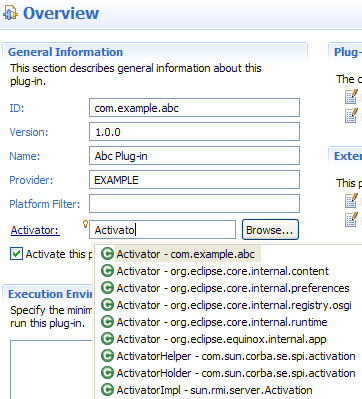
Field validation in plug-in and product editors
During validation, form fields are decorated according to problem severity and provide status messages via tool tips.
All status messages are qualified with a field label and rolled up into the form title header where they are available on mouse over.
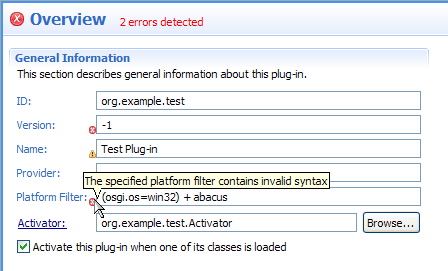
As with source page validation, the problem severity used by field validation is configurable on the Plug-in Development > Compilers preference page.
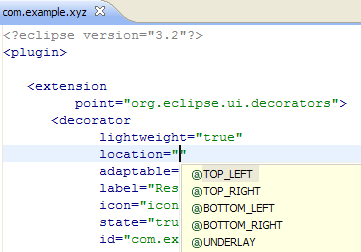
Content assist in plugin.xml
Content assist (Ctrl+Space) is now available on the plugin.xml source page to give you context-sensitive information as you create extensions and extension points.
Features include:
- completion proposals for extensions, extension points, attributes, and elements
- auto-generation of required elements and attributes
Note that the content assist can be activated without the need for a partial string. PDE uses extension point schemas to determine which elements and attributes are suitable for the current context.
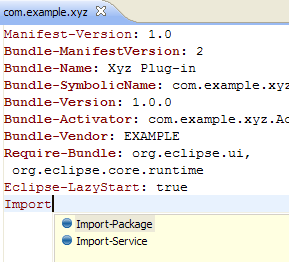
Content assist in MANIFEST.MF
- header names, attributes, and directives
- header values such as plug-in IDs, package names, and Java class names
- boolean and enumerated values for attributes and directives
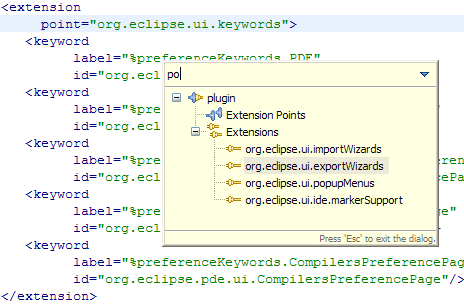
Quick outline in plug-in editor source pages
When editing a source in the plug-in manifest editor, pressing Ctrl+O or selecting Navigate > Quick Outline from the top level menu shows you a quick outline.
The quick outline has many of the sizing and filtering options that are available in the Java editor's quick outline.
Hyperlinking and open declarations
Hovering over attribute values on the plugin.xml page and pressing Ctrl+Left can be used to
- open resources and Java type declarations
- open extension point schema descriptions
- navigate from a translated key reference to that key in the properties file

Hyperlinking provides additional functionality on the MANIFEST.MF source page including:
- opening manifest editors for referenced plug-ins
- opening referenced packages
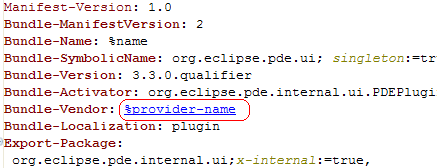
Hover support in plug-in manifest editors
The source pages in the plug-in manifest editors now provide a number of useful hovers. Hovering over an attribute in the plugin.xml shows the schema description for that attribute, while hovering over a manifest header shows the Javadoc for that header.
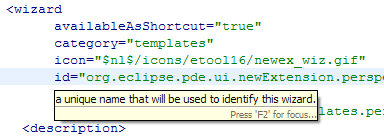
The hover support has also improved on the Extensions page of the plug-in manifest editor. Hovering over a translated attribute now shows the actual substituted value for that attribute.
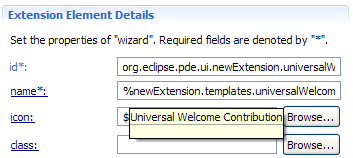
Code folding
The option to turn folding on and off can be found on the Plug-in Development > Editors preference page.
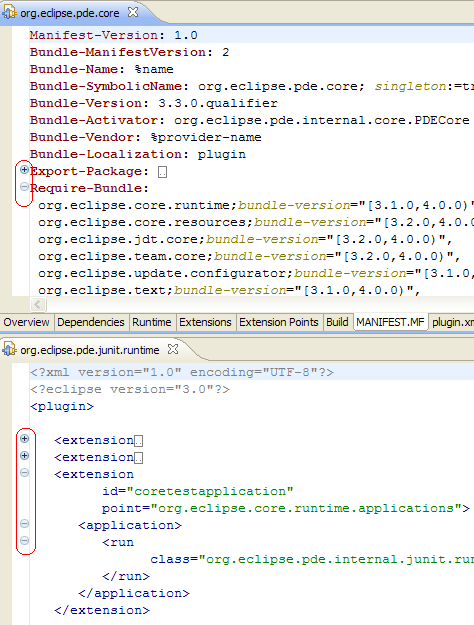
Code formatting
Line wrapping introduced by some packaging tools make the plug-in MANIFEST.MF file hard to read.
PDE now provides a Format action in the context menu of the MANIFEST.MF source page to format the contents of the file into something more human-readable.
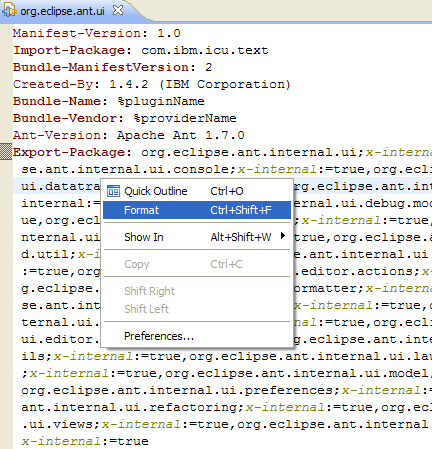
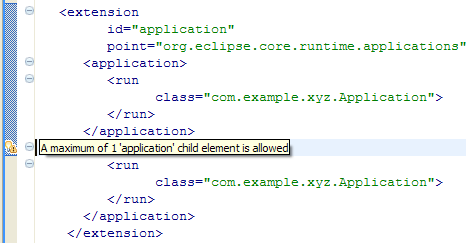
Stronger plugin.xml validation
The severity for this type of problem is set to Warning by default, and can be customized via the Plug-in Development > Compilers > Plug-ins > Illegal elements preference.
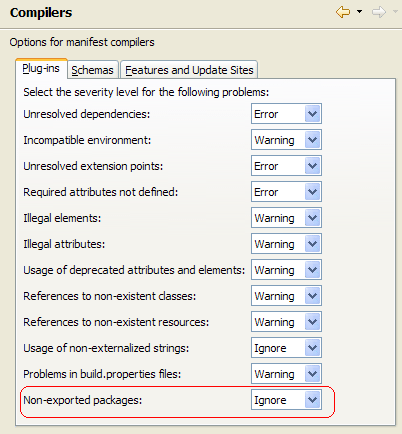
Flag for non-exported packages in the MANIFEST.MF file
PDE now provides a flag on the MANIFEST.MF file when the list of exported packages of the plug-in is incomplete. This feature is a useful reminder when you wish to expose all your plug-in code to downstream clients.
By default, the severity of this flag is set to IGNORE, but it can be raised to WARNING or ERROR at a global level via the Plug-in Development > Compilers > Plug-ins > Non-exported Packages preference. It can also be set on a per-project basis on the Plug-in Development > Compilers property page of a plug-in project.
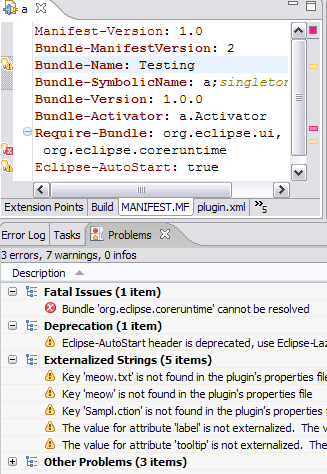
PDE problem categories
You can turn this feature on via Group by > PDE Problem Type from the drop down menu of the Problems view.
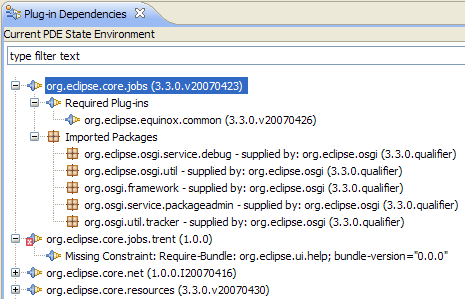
State of the plug-ins
The Plug-in Dependencies view, available under Window > Show View > Other > PDE > Plug-in Dependencies, has been enhanced to show you the state of every plug-in you have in your development environment.
For each plug-in, you get to see all its dependencies and the plug-ins supplying each of its imported packages.
The view now also serves as a valuable diagnostic tool that shows you the unsatisfied constraints that may prevent your plug-in from running and which may cause a chain reaction affecting other plug-ins.
New filtering capabilities include:
- focusing on unresolved plug-ins only
- showing leaf plug-ins only therefore helping you prune unnecessary plug-ins when assembling a product
Plug-in refactoring
The Rename function is available in the context menu of the Plug-ins view, the Plug-in Dependencies view and the MANIFEST.MF source page.
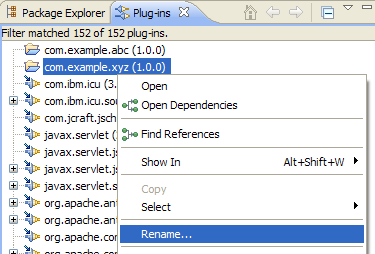
Plug-in refactoring may also take place as part of the regular project renaming action in the Package Explorer view (Refactor > Rename from the context menu) if the project name matches the plug-in ID.
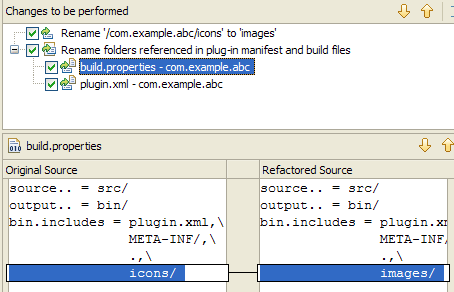
Plug-in manifest files participate in refactorings
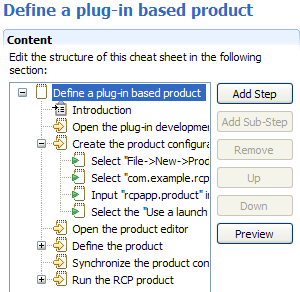
Cheat sheets guide users through a series of steps to achieve an overall task. PDE now provides a cheat sheet editor to let you compose cheat sheets, complete with embedded workbench commands and links to the Help documentation.
The editor also provides a Preview function that allows you to preview your work on the fly directly in the Cheat Sheets view.
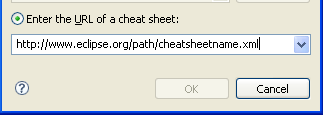
You can create a cheat sheet via File > New > Other... > User Assistance > Cheat Sheets.
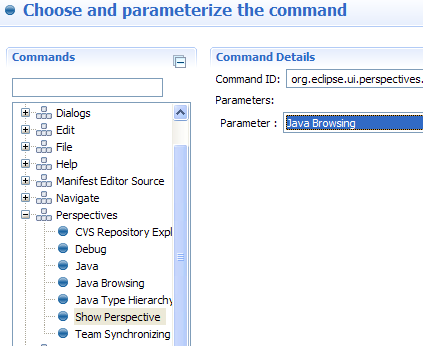
Command composer
Cheat sheets support the embedding of workbench commands allowing you to execute commands such as opening a particular perspective or a wizard in a script-like fashion.
The Command Composer dialog shows you a categorized list of available commands and their parameters, making it easy to compose, test, serialize, and embed commands into your cheat sheet.
The Command Composer can be invoked from the Command section of the cheat sheet editor.
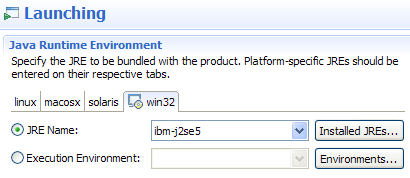
Bundling JREs in your RCP product
The Product editor now gives you the option to bundle a JRE with your exported Eclipse product. JREs can be specified on a per-platform basis.
The JRE will be bundled in a jre/ subdirectory inside the product, and it will be the default JRE used when the product runs.
This feature is useful if you want your product with a specific JRE or if the end user of your product does not have a JRE installed on their system.
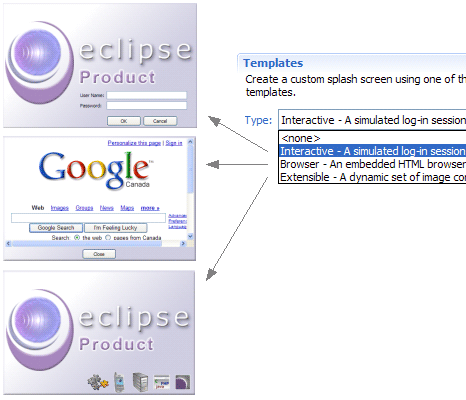
Custom splash screen templates
- Interactive: A simulated log-in session
- Browser: An embedded HTML browser
- Extensible: A dynamic set of image contributions
This feature is available in the Templates section on the Splash page of the product configuration editor.
Splash screen templates are also available in the New Extension wizard
when generating a new org.eclipse.ui.splashHandlers extension
on the Extensions page in the plug-in manifest editor.
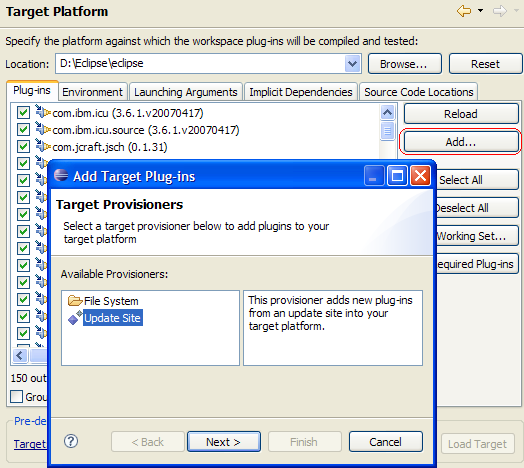
Target platform provisioning
PDE now allows the dynamic addition of plug-in locations to the target platform by simply pressing Add on the Plug-in Development > Target Platform preference page.
PDE provides two provisioners:
- a file system provisioner to augment the content of the target platform with plug-ins located in the file system.
- an update site provisioner that downloads and installs plug-ins into your target platform with a single click by simply pointing at an update site.
Additional types of provisioners can be declared via the org.eclipse.pde.ui.targetProvisioners extension
point.
Extensible launch shortcuts
org.eclipse.pde.ui.launchShortcuts extension
point to enable custom launch shortcuts and additional launch modes (e.g.
profile) to be integrated into the Testing section of
the plug-in manifest editor.
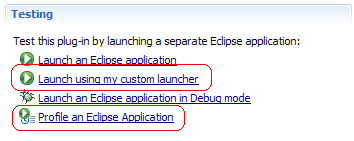
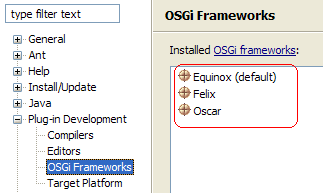
PDE now provides the org.eclipse.pde.ui.osgiFrameworks
extension point to enable the integration of additional OSGi frameworks
into the PDE bundle tooling.
If more than one OSGi framework is installed, the default can be set on the Plug-in Development > OSGi Frameworks preference page.
Testing against different OSGi frameworks is as easy as selecting that framework in the OSGi Framework launch configuration.
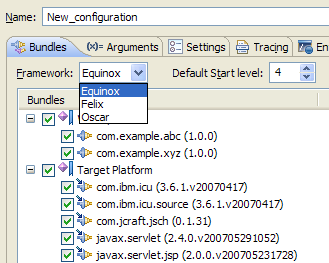
Note that PDE only provides the Equinox OSGi framework extension.
Hello, World - 3.3 edition
In Eclipse 3.3, the Platform introduced a new way to contribute menu and toolbar items to the workbench. See this new support in action by selecting the Hello, World Command template in the New Plug-in Project wizard, available under File > New > Project... > Plug-in Development > Plug-in Project.
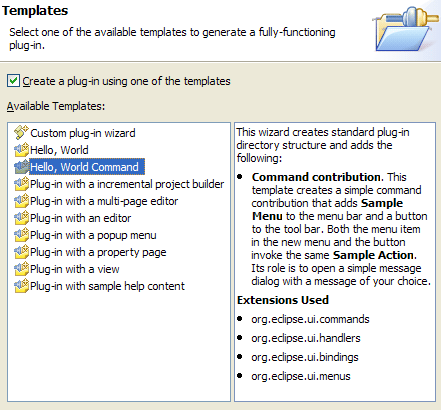
The New Plug-in Project wizard, available under File > New > Project... > Plug-in Development > Plug-in Project, provides new templates demonstrating the usage and implementation of programmatic OSGi services.
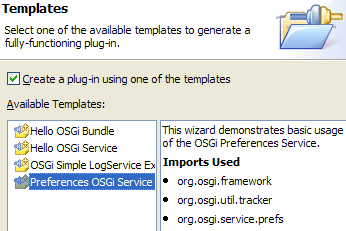
The templates are available when the option to target an OSGi framework is selected on the first page of the wizard.
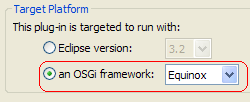
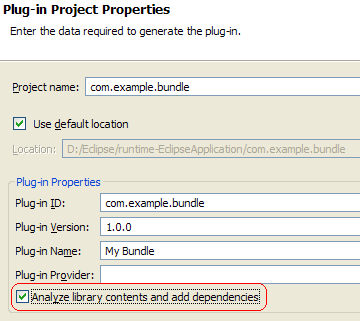
Analyze dependencies for JAR archives
Plug-ins targeted to run with an OSGi framework will have their dependencies specified with Import-Package statements, while plug-ins targeted to run with Eclipse will have theirs specified with Require-Bundle statements.
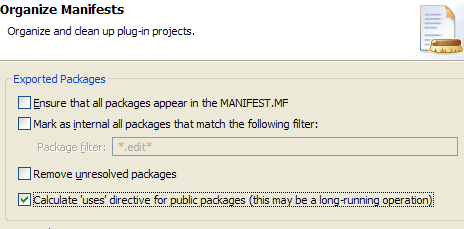
Uses directive calculation
The uses directive is important because it models inter-package dependencies to ensure that consistent class spaces are calculated for each bundle. This helps prevent ClassCastExceptions when multiple versions of a package or bundle are installed in the Framework.
The calculation can be initiated from the Organize Manifests wizard (PDE Tools > Organize Manifests... from the context menu of plug-in projects) or the Calculate Uses button in the Exported Packages section on the Runtime page of the plug-in manifest editor.
Multi-version support for build contributions
GET fetch support
platform.xml handling